A more complete NO/ONOO- cycle diagram. Central to the figure are the

Download scientific diagram | A more complete NO/ONOO- cycle diagram. Central to the figure are the reciprocal interactions between peroxynitrite, abbreviated as PRN and tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) depletion. Also indicated is the ATP depletion produced by peroxynitrite, superoxide and nitric oxide. And in the upper left corner, TRP represents the three TRP receptors, TRPV1, TRPA1 and TRPM2, each of which is stimulated via distinct mechanisms by oxidative stress. Each arrow in the figure represents one or more mechanisms by which one element of the cycle stimulates another element of the cycle. Figure and legend is taken from the author’s web site with permission. from publication: The NO/ONOO-Vicious Cycle Mechanism as the Cause of Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis | Cases of chronic fatigue syndrome/mylagic encephalomyelitis (CFS) are reported to be initiated by nine different short-term stressors, each of which increase levels of nitric oxide in the body. Elevated nitric oxide, acting through its oxidant product, peroxynitrite, | Chronic Fatigue Syndrome, Clinical Protocols and Clinical Studies | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

A more complete NO/ONOO- cycle diagram. Central to the figure are the

Rational Design of a Theranostic Agent Triggered by Endogenous Nitric Oxide in a Cellular Model of Alzheimer's Disease

Oxidative Stress-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction in Cardiovascular Diseases

Diagramatic representation of the bell-shaped relationship between NO ⋅

Multiphase Kinetic Modeling of Air Pollutant Effects on Protein Modification and Nitrotyrosine Formation in Epithelial Lining Fluid
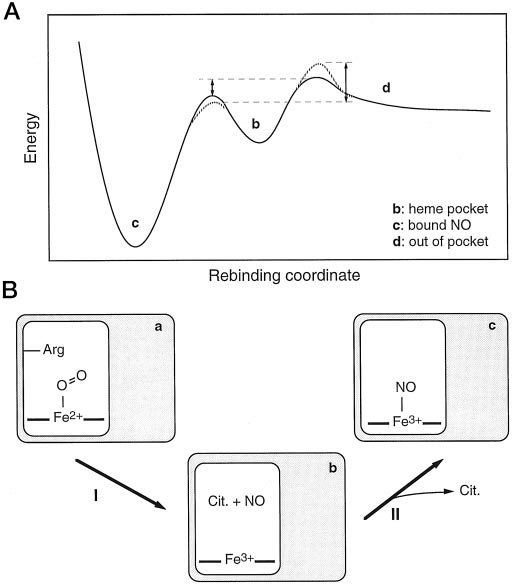
A, putative energy curve model for three main stages of NO rebinding to

Theoretical investigation of oxidation of NO (NO + ½ O2 → NO2) on surfaces of nickel-doped nanocages (Ni–C60 and Ni–B30N30) - ScienceDirect

Biomolecules, Free Full-Text
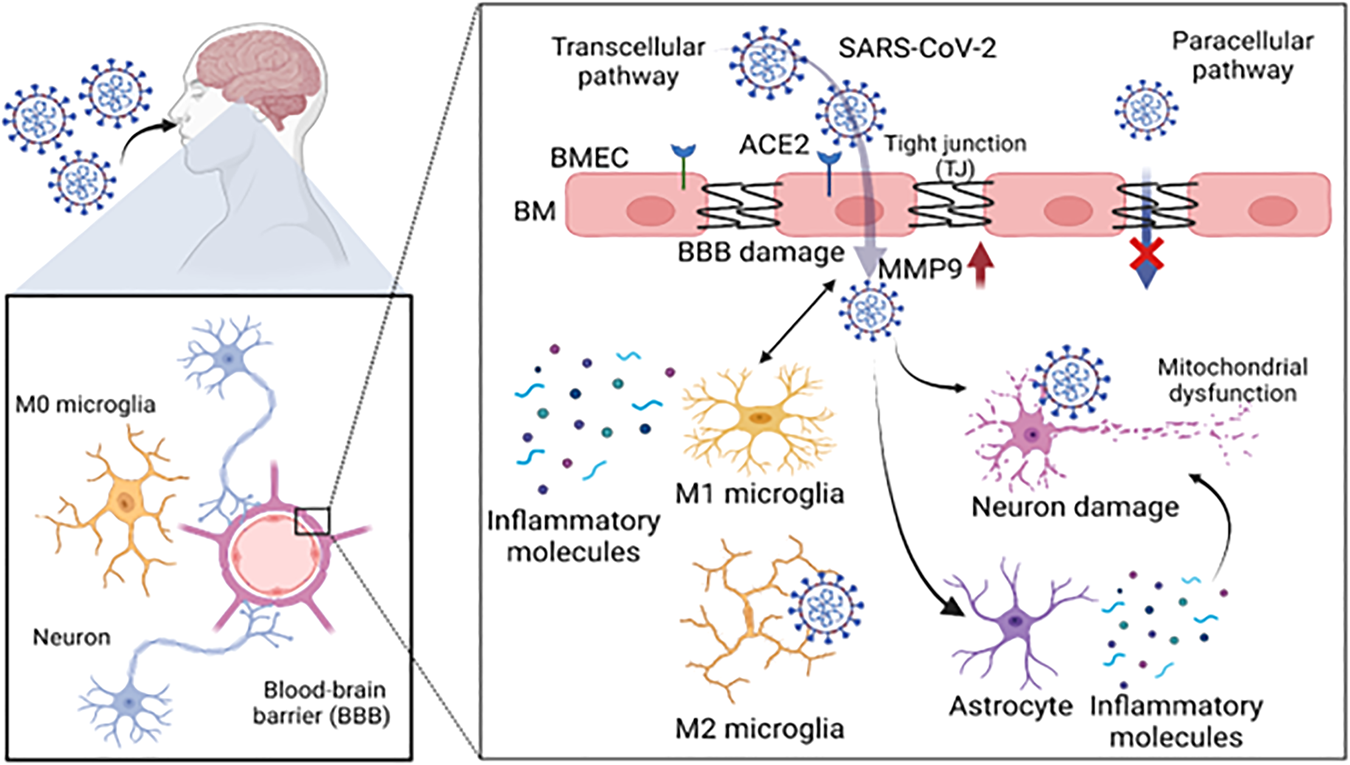
Immune landscape and redox imbalance during neurological disorders in COVID-19