Hof1 plays a checkpoint-related role in MMS-induced DNA damage response in Candida albicans


Nucleotide Excision Repair Protein Rad23 Regulates Cell Virulence Independent of Rad4 in Candida albicans

Critical Role of DNA Checkpoints in Mediating Genotoxic-Stress–induced Filamentous Growth in Candida albicans

Functional connections between cell cycle and proteostasis in the regulation of Candida albicans morphogenesis - ScienceDirect
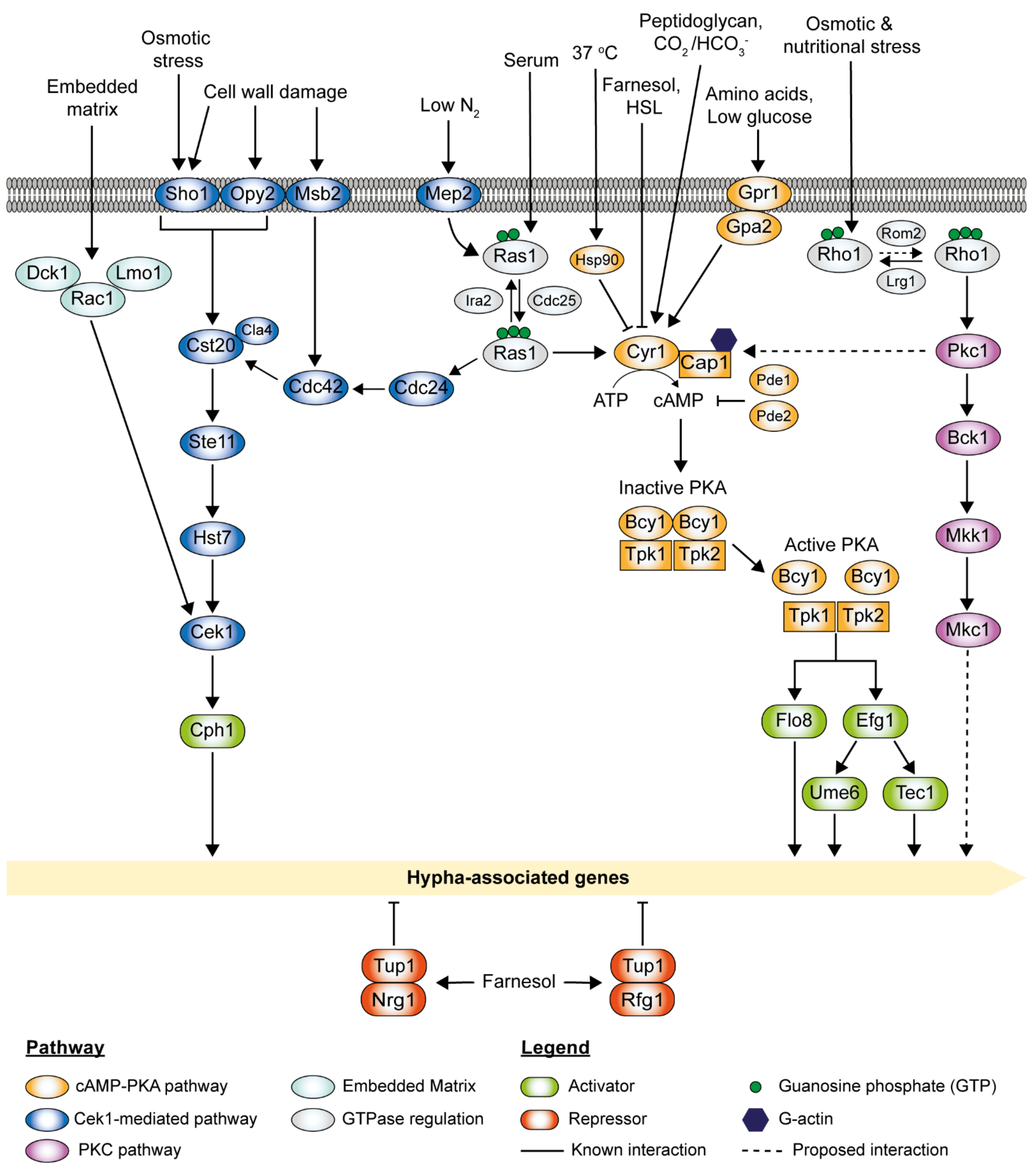
Pathogens, Free Full-Text

Molecular Microbiology, Microbiology Journal

Rad53- and Chk1-Dependent DNA Damage Response Pathways Cooperatively Promote Fungal Pathogenesis and Modulate Antifungal Drug Susceptibility

The Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAD9, RAD17 and RAD24 genes are required for suppression of mutagenic post-replicative repair during chronic DNA damage. - Abstract - Europe PMC

A J Domain Protein Functions As A Histone Chaperone To, 56% OFF

Hof1 plays a checkpoint-related role in MMS-induced DNA damage response in Candida albicans

Nucleotide Excision Repair Protein Rad23 Regulates Cell Virulence Independent of Rad4 in Candida albicans

A Noncanonical DNA Damage Checkpoint Response in a Major Fungal Pathogen

Analysis of hof1 phenotypes in the absence of Bni1 or Bnr1 function.

A Noncanonical DNA Damage Checkpoint Response in a Major Fungal Pathogen

IJMS, Free Full-Text

Hof1 plays a checkpoint-related role in MMS-induced DNA damage response in Candida albicans