Isolation of CAR T cells and its interaction with tumor-associated

Download scientific diagram | Isolation of CAR T cells and its interaction with tumor-associated antigens (TAA) in solid tumors. T cells are collected from patients’ peripheral blood via leukophores and are designed to express chimeric antigen receptors to tumor-specific antigens. These cells proliferate before being re-injected. After injection, autologous CAR-engineered T cells detect TAA and binds to its corresponding ligand, leading to the secretion of cytokines and the interaction of some apoptosis-related ligands, which ultimately leads to the destruction of tumor cells from publication: CAR T cells in solid tumors: challenges and opportunities | Background CARs are simulated receptors containing an extracellular single-chain variable fragment (scFv), a transmembrane domain, as well as an intracellular region of immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs) in association with a co-stimulatory signal. Main | CAR T Cells, Solid Tumors and Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Regression of Glioblastoma after Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy

Single-Cell Analyses Identify Brain Mural Cells Expressing CD19 as Potential Off-Tumor Targets for CAR-T Immunotherapies - ScienceDirect
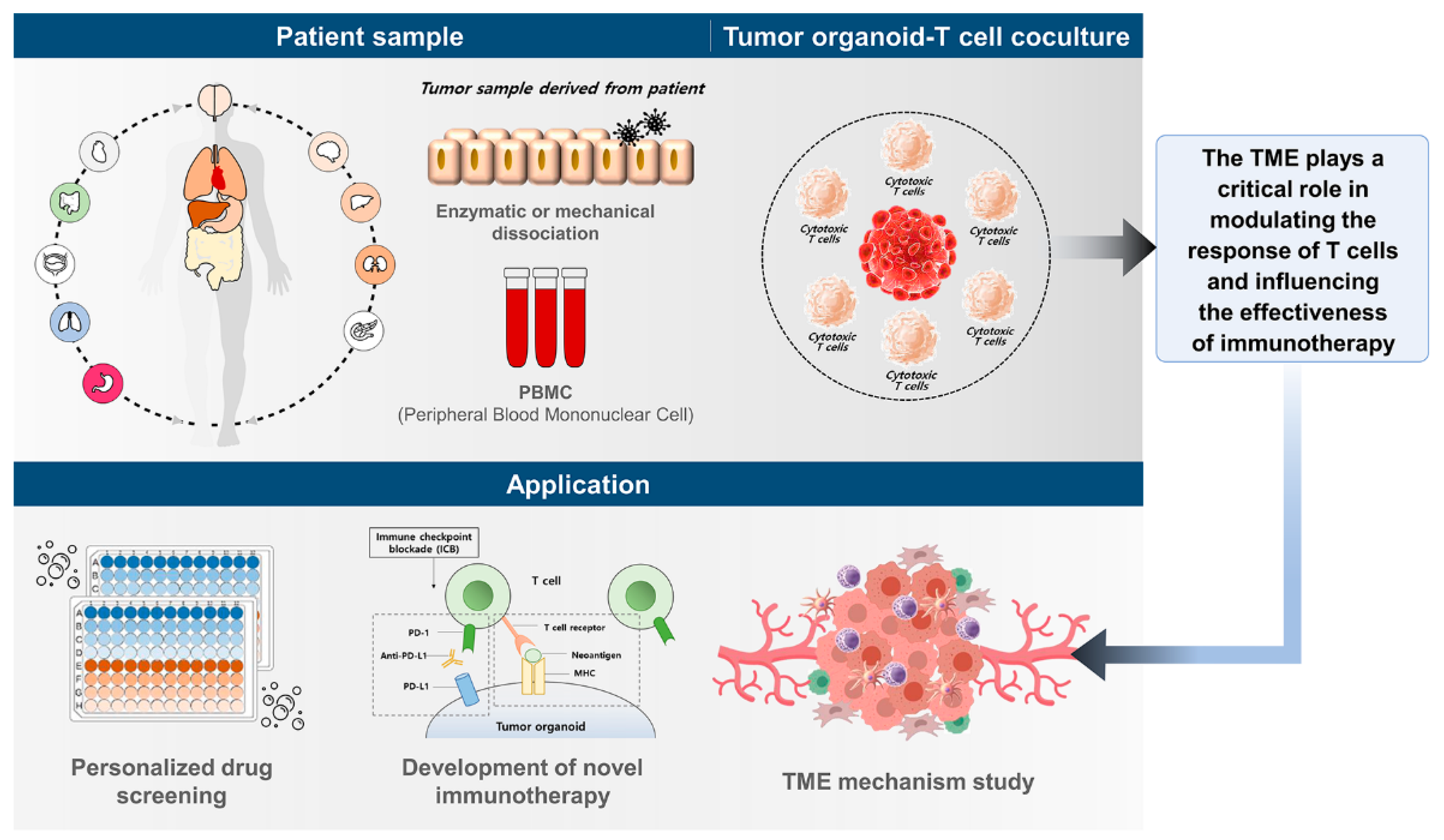
IJMS, Free Full-Text
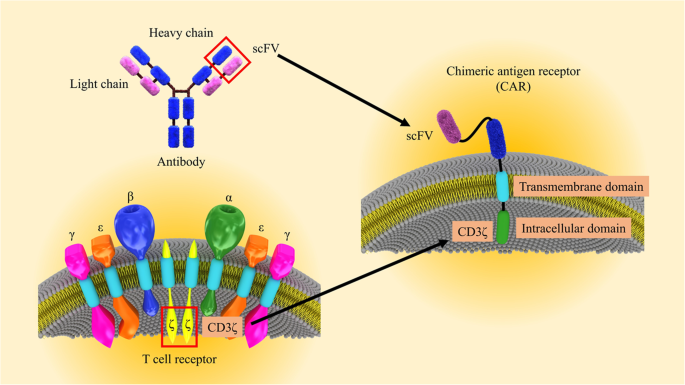
CAR T cells in solid tumors: challenges and opportunities, Stem Cell Research & Therapy

Bioorthogonal Equipping CAR-T Cells with Hyaluronidase and Checkpoint Blocking Antibody for Enhanced Solid Tumor Immunotherapy

TCR Redirected T Cells for Cancer Treatment: Achievements, Hurdles, and Goals. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Universal allogeneic CAR T cells engineered with Sleeping Beauty transposons and CRISPR-CAS9 for cancer immunotherapy - ScienceDirect

illustrates the limitations of CAR-T cell therapy and the challenges it

Precision Tumor Recognition by T Cells With Combinatorial Antigen-Sensing Circuits: Cell